Testing Progress
This document explains the tests already implemented for NAVIGO.
Implemented Unit Tests
1. useStepCounter.test.ts
Purpose:
Verifies that the step counter logic correctly increments when motion events are fired, simulating real-world walking.
How It Works:
- Uses
renderHookto mountuseStepCounter.
const { result } = renderHook(() => useStepCounter());
- Simulates a walking step by dispatching a
DeviceMotionEventwith acceleration values.
act(() => {
window.dispatchEvent(
new DeviceMotionEvent("devicemotion", { acceleration: { x: 2, y: 1, z: 0 } })
);
});
- Asserts that the step count (
steps) increased beyond zero.
expect(result.current.steps).toBeGreaterThan(0);
Ensures that student movement across campus is tracked as steps, which is critical for quest progress.
2. QuestTracker.test.tsx
Purpose:
Verifies that the QuestTracker component correctly shows the distance between the player’s current location and the quest’s target location.
How It Works:
- Defines a quest location.
const questLocation = { lat: 48.8566, lng: 2.3522 };
- Mocks
navigator.geolocationto return user’s position.
global.navigator.geolocation = {
getCurrentPosition: vi.fn((success) =>
success({ coords: { latitude: 51.5074, longitude: -0.1278 } }) // London
),
watchPosition: vi.fn(),
clearWatch: vi.fn(),
};
- Renders the
QuestTrackercomponent with the quest location.
render(<QuestTracker questLocation={questLocation} />);
- Checks that the UI outputs
"Distance:".
expect(await screen.findByText(/Distance:/)).toBeTruthy();
Confirms that students can see how far they are from a quest checkpoint, ensuring gameplay accuracy.
3. useGeolocation Hook
Purpose:
Provides a reusable hook that continuously tracks the player’s geolocation and handles errors.
How It Works:
- Uses
useStateto storepositionanderror.
const [position, setPosition] = useState<NormalizedPosition | null>(null);
const [error, setError] = useState<GeolocationPositionError | null>(null);
- Checks for geolocation support and reports an error if not supported.
if (!navigator.geolocation) {
setError({ message: "Geolocation not supported" } as GeolocationPositionError);
return;
}
- Uses
navigator.geolocation.watchPositionto track live GPS coordinates. - Updates position with latitude, longitude, and accuracy.
const watcher = navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(
(pos) => {
setPosition({
lat: pos.coords.latitude,
lng: pos.coords.longitude,
accuracy: pos.coords.accuracy,
});
},
(err) => setError(err),
{ enableHighAccuracy }
);
- Cleans up with
clearWatchwhen the component unmounts.
return () => navigator.geolocation.clearWatch(watcher);
- Tracks whether a student is physically present at a quest checkpoint.
- Compares live position with Firestore-stored quest coordinates.
- Ensures quests only complete when the player is at the correct location.
4. geo.test.ts (Haversine Formula)
Purpose:
Tests the haversineDistanceMeters utility, which calculates distance between two GPS coordinates.
How It Works:
- Test 1: Verifies that identical coordinates return a distance of
0.
it("calculates distance between two identical points as 0", () => {
const a = { lat: 0, lng: 0 };
const b = { lat: 0, lng: 0 };
expect(haversineDistanceMeters(a, b)).toBeCloseTo(0, 5);
});
- Test 2: Verifies that the calculated distance between London and Paris is ~343 km.
it("calculates approximate distance between two known points", () => {
// London (51.5074, -0.1278) to Paris (48.8566, 2.3522) ≈ 343 km
const london = { lat: 51.5074, lng: -0.1278 };
const paris = { lat: 48.8566, lng: 2.3522 };
const meters = haversineDistanceMeters(london, paris);
expect(meters / 1000).toBeGreaterThan(340);
expect(meters / 1000).toBeLessThan(350);
});
- Used to check if a student is “close enough” (e.g., within 50 meters) to a quest location.
- Ensures the quest validation logic is accurate and fair.
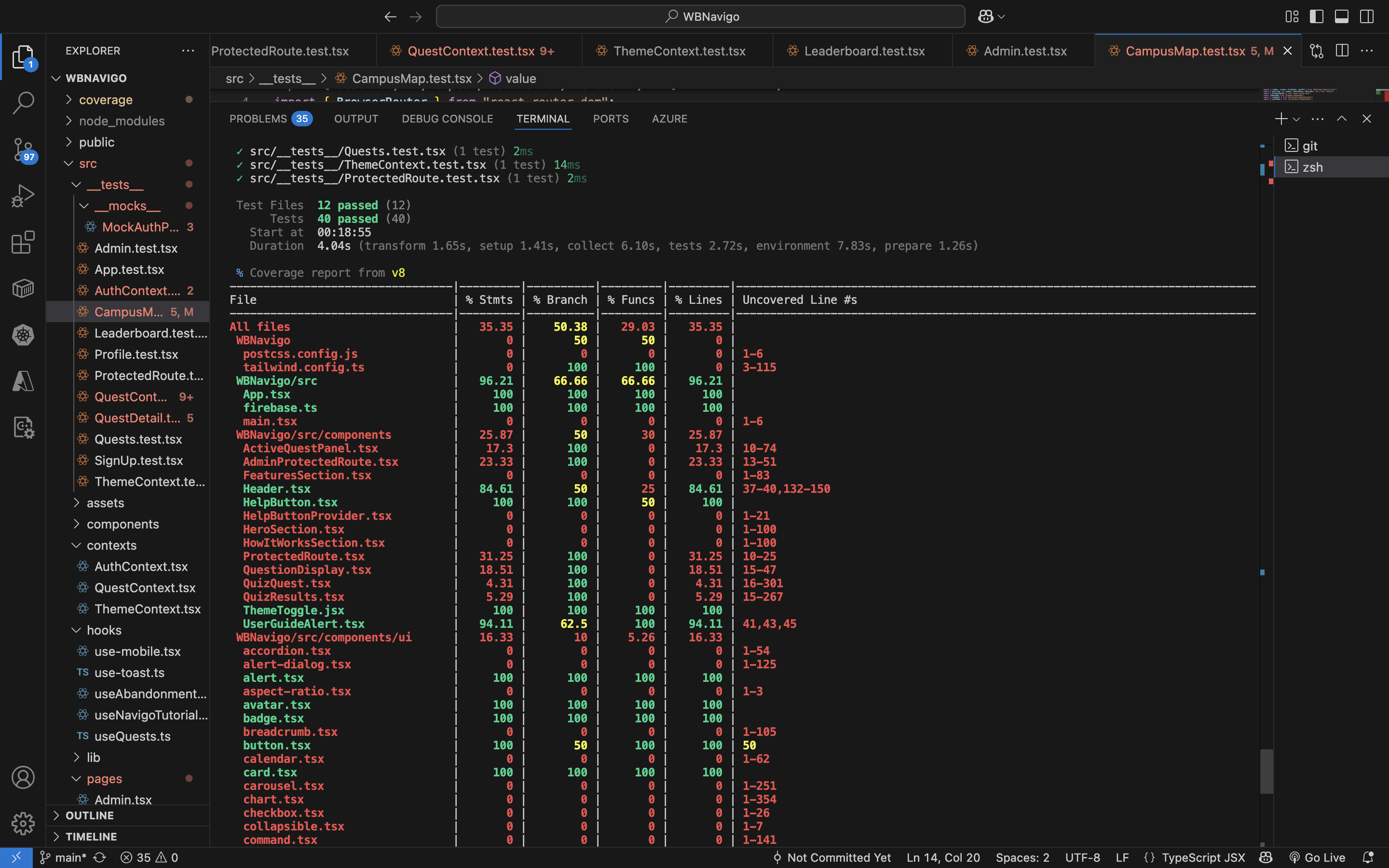
##Captured Coverage
The captured coverage is 35%